Sleep is an essential biological process crucial for optimal brain function. Psychologically, it supports cognitive processes like memory consolidation, problem-solving, and emotional regulation. Biologically, sleep enables cellular restoration, neural pruning, and hormone regulation. Insufficient sleep disrupts these functions, impairing attention, learning, mood, and increasing the risk of mental health disorders.


How the Immune Response is Reinforced
- NEMURI or NUR → antimicrobial peptide secreted from neurons that also promotes sleep
- Sleep is coupled with immune response in fighting infections
- Why is sleep so important for brain health?
-
- Appropriate sleep helps clear those proteins but at the same time it can disrupt sleep circuits (feedback loop).

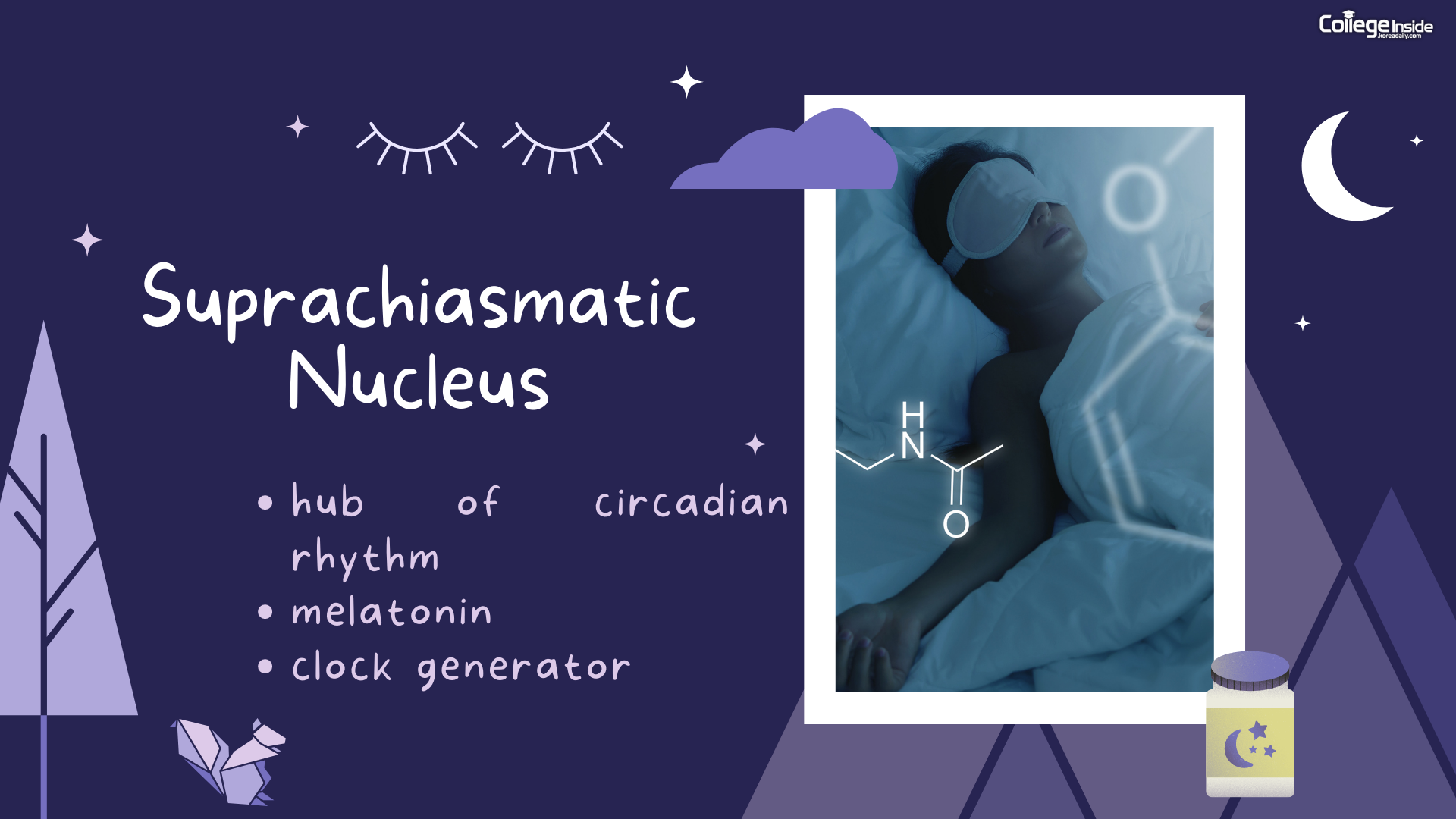
- It is important to note that both homeostatic and circadian control work in parallel not competition. There are two mechanisms that control our sleep.
- Homeostatic control – weight is at a set point.
- Process S
- build sleep pressure as we are awake and dissipates as we sleep (vast drop while sleeping)
- Process C
- static
- Process S
- Circadian regulation
- don’t have to expend energy when it is not necessary (every cell is under circadian regulation)
- clock genes
- EVOLUTIONARY PERSPECTIVE on circadian rhythms..
- clock is informed by forward input into the clock (example: light, activity patterns eating).
- EVOLUTIONARY PERSPECTIVE on circadian rhythms..
- clock genes
- don’t have to expend energy when it is not necessary (every cell is under circadian regulation)

Sleep abnormalities can accelerate the Alzheimer’s disease pathology due to the crucial role sleep plays in clearing away toxic substances from the brain, including beta-amyloid plaques associated with Alzheimer’s. Disrupted sleep patterns can impair the glymphatic system, responsible for waste clearance, leading to the accumulation of harmful proteins. This buildup accelerates the progression of Alzheimer’s disease, impacting memory, cognition, and overall brain health.
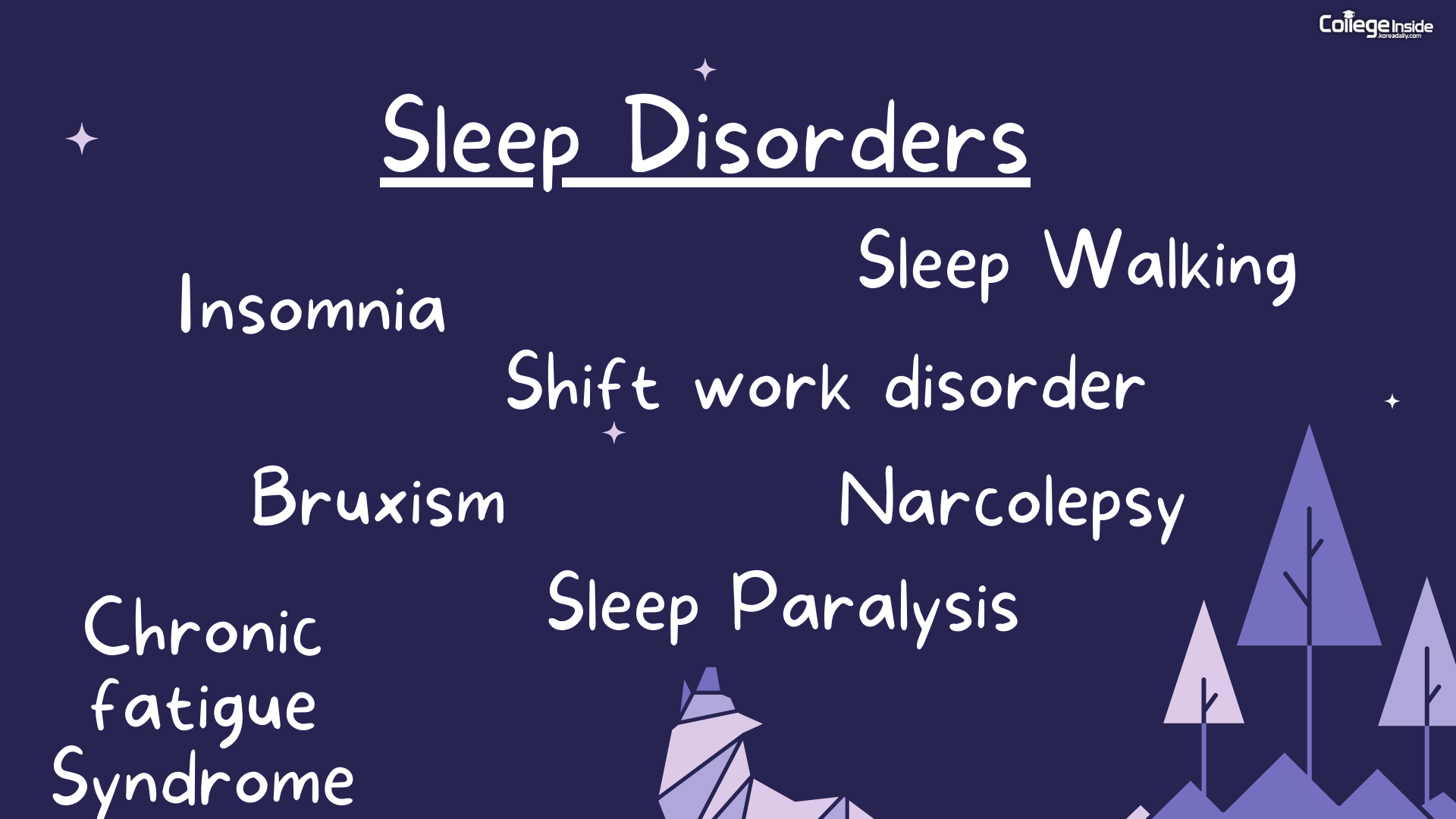
Sleep disorders can develop due to various reasons. They may arise from underlying medical conditions like sleep apnea, insomnia, or restless leg syndrome (as listed above). Moreover, lifestyle choices, such as irregular sleep schedules, excessive caffeine intake, or high-stress levels, can contribute significantly.
Getting some sleep is not sufficient but enough, uninterrupted sleep is necessary for our overall well-being. It is an essential biological process that provides our bodies and minds with the necessary rest, restoration, and recovery. Psychologically, sleep plays a crucial role in cognitive abilities, emotional stability, and memory consolidation. Biologically, it supports cellular maintenance, waste removal, and hormone regulation. Recognizing the importance of sleep and prioritizing quality rest is essential for maximizing our physical, mental, and emotional functioning.